Table of Contents
What is NPA(Non Performing Asset)?
NPA or Non-performing Assets are those types of loans in the banking sector for which the borrower will not pay the interest amount or principal amount for more than 90 days. For this type of loan, the banker thinks the loan agreement is broken, and the borrower cannot pay the loan amount. In easy terms, if the clients will not pay the principal amount and interest for a particular period, then such loans are known as Non Performing Assets. In India, the timeframe given for this asset as NPA is 90 days.
Non-Performing Assets Example
For example, Company ABC has taken credit of 5lakhs from Bank XYZ on which it has to repay 15000 of interest every month for one year. If the company ABC will not pay the interest amount or Principal amount for three consecutive months, i.e., 90 days. Then the Bank XYZ has to consider the loan as NPA in their balance sheet.
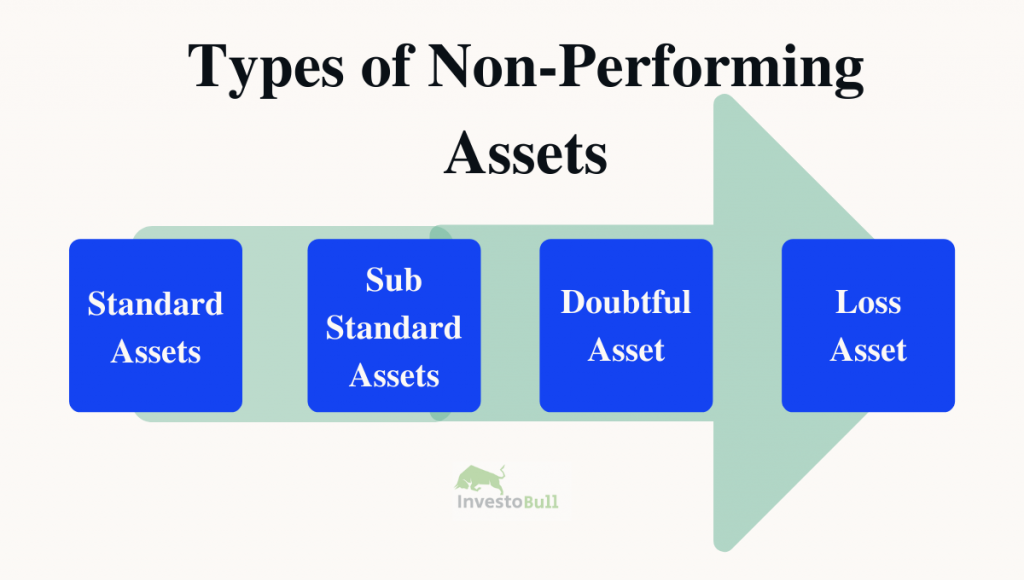
NPAs are classified into four types.
Standard Assets:
It is a performing asset that generates constant income and pays back the loans before the due date. Therefore, these assets have a reasonable risk and are not considered as NPAs.
Sub-Standard Assets:
NPAs that have been not paying the interest amount or principal amount for upto 12 months or one year comes under sub-standard assets.
Doubtful Assets:
Non-performing assets are in the doubtful debts category, have not paid the interest amount or principal amount for more than 12 months to 36 months. Lenders normally have doubts that the borrower will pay back the full loan or not. Therefore, this NPA will severely affect the bank’s profile.
Loss Assets:
These are non-performing assets that do not pay the interest amount or principal amount for more than three years. With this class, the banks are unable to recover the amount. Finally, banks will register this loan amount as a loss on their balance sheet. The entire loan amount will close completely.
Reasons of NPAs
Willful Defaults:
One of the main causes behind NPA is the negligence of the borrower. A person who is not paying any interest amount or principal amount to the bank even if he is in a position to pay. The best example of willful defaults is Kingfisher Airlines Ltd.
Financial conditions –
The Financial condition of a country influenced by natural disasters or any other reason may lead to NPA.
No risk management –
Gambling is one of the significant reasons behind NPA. Sometimes lenders grant loans to borrowers with poor credit records. There will be high chances of failure in these cases.
Mis-management –
Few people corrupt the bank officials to approve their loans, and they are not willing to pay back the loan amount. However, misuse of funds can also lead to NPA’s.
Diversion of funds –
Many borrowers redirect the acquired funds to personal uses other than specified in loan documents. It is tough to retrieve from this sort of borrower.
What is the impact of NPAs?
- Bank’s profit will decrease, which they get in the form of interest.
- It can affect a bank liquidity position and reputation.
- Negatively influences the lender’s financial balance sheet.
- Because of NPA, Banks will increase their interest to keep the profit margin.
- Redirecting funds from the right schemes to the bad schemes.
- Customers do not get decent returns.
What is Gross NPA?
Gross NPA is a term used by bank sectors. It means the total value of outstanding NPAs in the borrower account. According to RBI guidelines, once the borrower account is listed as NPA, interest will not be deducted to the NPA account and allocated as profit.
Banks give credit to their clients who are unable to pay within 90 days. After that, they will consider it as non-performing assets because they are not getting any principal or interest amount.
What is Net NPA?
Net NPA is a term used by bank sectors. It can be defined as Gross NPA – (Interest+Insurance from DICGC or ECGC + Total provision held). Here banks tend to get an alert amount to embrace unpaid debts.
Therefore, if one subtracts the outstanding debts, the resulting value is known as net non-performing assets (Net NPA)




















Leave a Reply